SUSPENSION TERMS GLOSSARY
The Ksport Guide to Understanding Suspension Terminology
Suspension terminology can be quite intimidating, especially if you aren’t well versed in automotive language. But, even if you are, there might be a few things here and there you’ve forgotten or can’t quite accurately explain. No need to worry though, we compiled a compact glossary of important suspension terms to use in those times of need.
Suspension Terms A to Z
A
- Air Bump – They help protect the vehicle and suspension components from hard bottom-outs and they also play a critical role in end-stroke damping.
- Air Shock – This allows you to increase the ride height of your vehicle, helping to bring it to the level when hauling a heavy load. When air shocks are installed with heavier springs on a truck chassis, they help to increase the useful load of the vehicle. Air shocks use a large diameter shaft to act as a spring and damper.
B
- Bleed – A valve through the piston where oil can pass through. Bleeding is ridding the brake system of trapped air, but some of the old fluid is expelled as well.
- Balancing – The process of equalizing the weight of the combined tire and wheel assembly so that it spins smoothly at high speed.
- Ballast – Something that is added to a car to bring it up to the minimum weight.
C
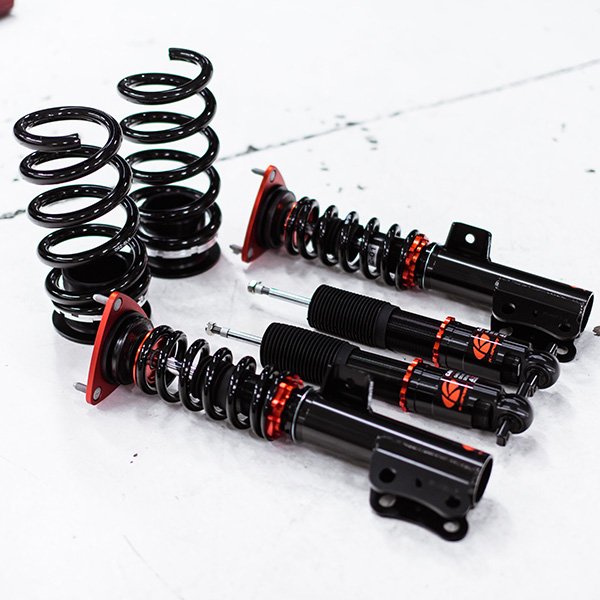
- Coilover – An automobile suspension device used to prevent the chassis from bottoming out, support each individual wheel on the vehicle, and to mitigate or reduce body roll when taking turns and cornering, particularly at higher speeds.
- Control Arm– A hinged suspension link between the chassis and the suspension upright or hub that carries the wheel.
- Cornering – A measurement of the force exerted on the vehicle’s center of gravity.
- Corner weight – The weight of one corner of the vehicle. Left and right sides may be slightly different.
- Crossmembers – This supports the underside of your car and carries the weight of the engine and transmission.

D
- Damper – A mechanical or hydraulic device designed to absorb and damp shock impulses.
- Double Wishbone – An independent suspension design using two wishbone-shaped arms to locate the wheel.
- Dual Rate – A spring setup using two stacked springs, commonly with a cross over point when the upper spring stops collapsing and transitions fully to the lower spring rate.

E
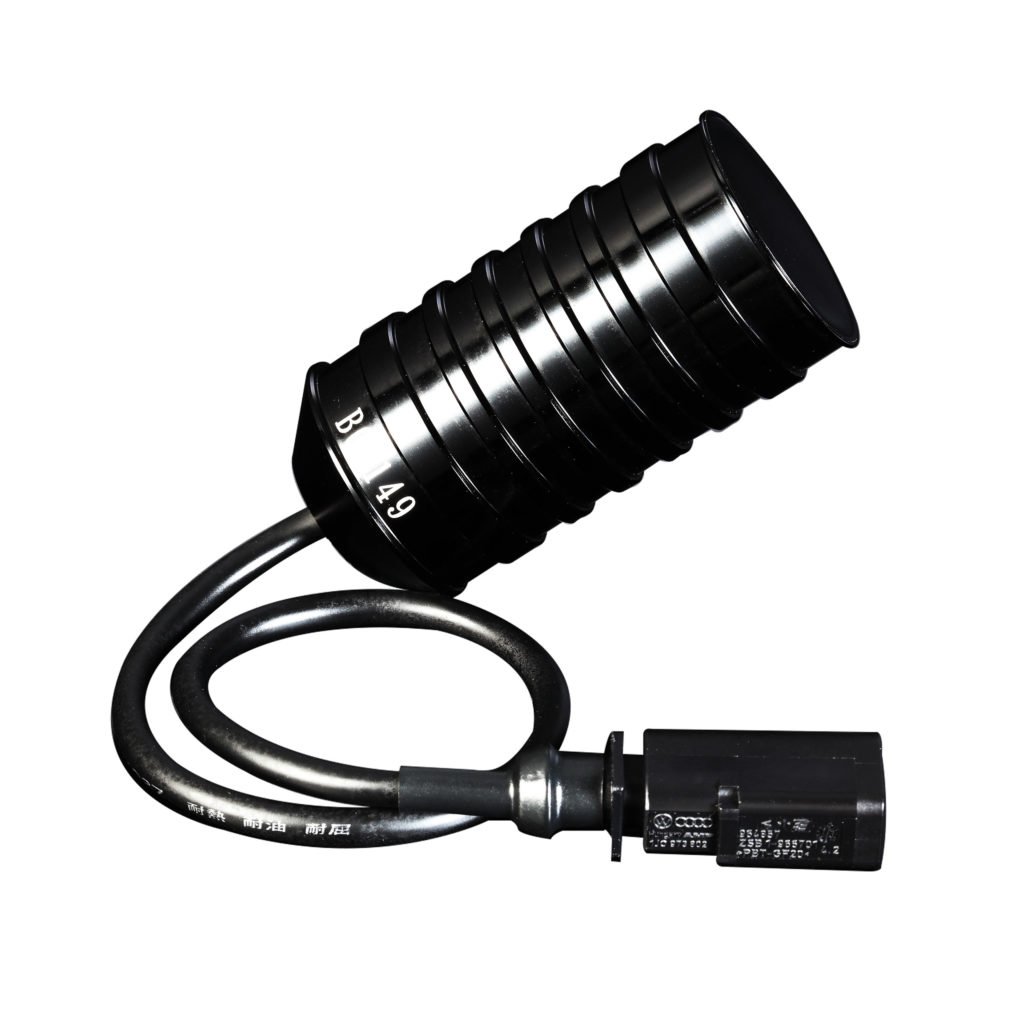
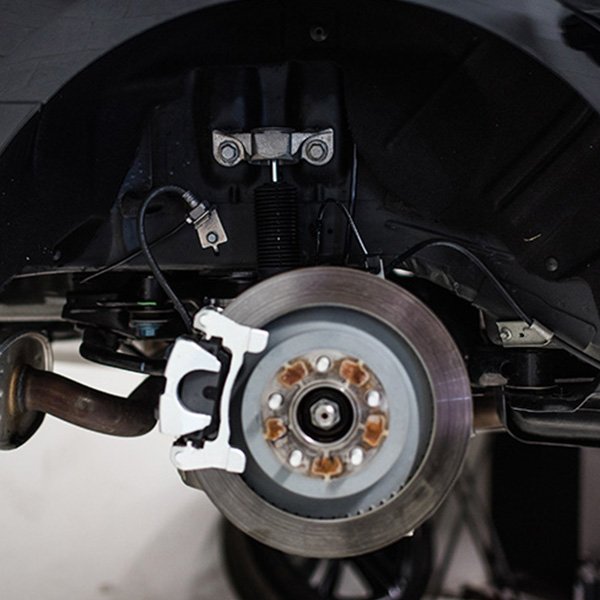
- Electronic Damping Kit – This suspension term comes into play when a suspension upgrade is completed some vehicles may not recognize the coding of the new components, resulting in service lights, error messages and potential ECU failure. Electronic Damping Cancellation kits eliminate the trouble codes that exist when upgrading suspension on a vehicle with electronically regulated dampers and prevent ECU failure by canceling the factory damper signal which would normally result in a service light.
F
- Flutter stack – This is when one or more small diameter disks are inserted between larger diameter disks, allowing the soft initial disks to bend up into the stiffer primary disks. The result is a progressive damping curve which is more tunable.
G
- Grip – A term describing the total cornering envelope of a race car by the friction component of the tire, the mass of the machine and the downforce generated.
H
- Helper Springs – Enhancement springs that support the main spring by keeping it in contact with its spring perch.

I
- Inboard – Suspension spring system where the spring/damper is mounted near or within the chassis via rocker and pull/push rod system.
- Instant Center – An imaginary point about which the chassis or a suspension member rotates in a given (instant) position.
J
- Jounce – The upward suspension travel that compresses the spring and shock absorber.
L
- Lifting – A modification to a vehicle to raise the ride height. It is done for the purpose of improving the off-road performance of SUVs or trucks and other off-road vehicles, or for cosmetic purposes.
- Linear Rate Coil Spring – A coil spring with equal spacing between the coils, one basic shape, and constant wire diameter having a constant deflection rate regardless of load.
- Lowering Springs – Springs will often allow you to lower your car without sacrificing the soft stock suspension feel. A proper spring and shock set up can make your car lower and slightly stiffen up your suspension, which provides a cheaper alternative to coilovers with nearly similar performance. Check out our blog, Lowering Springs vs Coilovers to learn which one is right for you.
M
- Motion Ratio – describes the amount of shock travel for a given amount of wheel travel. Mathematically it is the ratio of shock travel and wheel travel.
O
- Oversteer – This occurs when a car turns by more than the amount commanded by the driver.
P
- Preload – A measurement of how much a spring is compressed at full extension of the shock.
- Push Rod – an inboard suspension component that functions as a portal for transferring lubricating oil though the valve lifter and up to the cylinder head.
- Percent slip – The difference between theoretically calculated forward speed based on angular speed of the rim and rolling radius, and the actual speed of the vehicle.
R
- Rebound – This regulates the speed at which your fork or shock recovers, or bounces back, from an impact and returns to its full travel.
- Rocker – An inboard suspension component used to transfer wheel loads to the spring. This can be an entire suspension control arm or a component between the pull/push rod and spring.
- Roll Axis – A line connecting the rear suspension roll center with that of the front.
S
- Section Width – the measurement of the tire’s width from its inner sidewall to its outer sidewall at the widest point.
- Short-Long-Arm – also known as an unequal length double wishbone suspension. The upper arm is typically an A-arm, and is shorter than the lower link, which is an A-arm or an L-arm, or sometimes a pair of tension/compression arms.
- Slip Angle – The angle between the direction in which a wheel is pointing and the direction in which it is actually traveling.
- Smoothie – A smooth body shock.
- Solid Axle – A dependent suspension design, in which a set of wheels is connected laterally by a single beam or shaft.
- Spring Rate – the amount of weight that is needed to compress a spring one inch.
- Sprung Weight – the portion of the vehicle’s total mass that is supported by the suspension, including in most applications approximately half of the weight of the suspension itself.
- Stabilizer Bar – A part of many automobile suspensions that helps reduce the body roll of a vehicle during fast cornering or over road irregularities. It connects opposite wheels together through short lever arms linked by a torsion spring.
- Squat – Vehicle pitch under acceleration.
T
- Toe Angle – The symmetric angle that each wheel makes with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, as a function of static geometry, and kinematic and compliant effects.
U
- Unsprung Weight – weight of everything below the springs such as tires, wheels, solid axles, and roughly 1/3 the weight of connecting members.

W
- Wheelbase – The horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels.
- Wheel Rate – This is the spring rate at the wheel, it takes into account the suspension motion ratio and is useful for comparing across vehicles.
Y
- Yaw – The angle between vehicle centerline and actual direction of motion around a turn.
We hope these suspension terms, whether completely new or just a refresh, help you navigate your vehicles suspension and upgrades!
